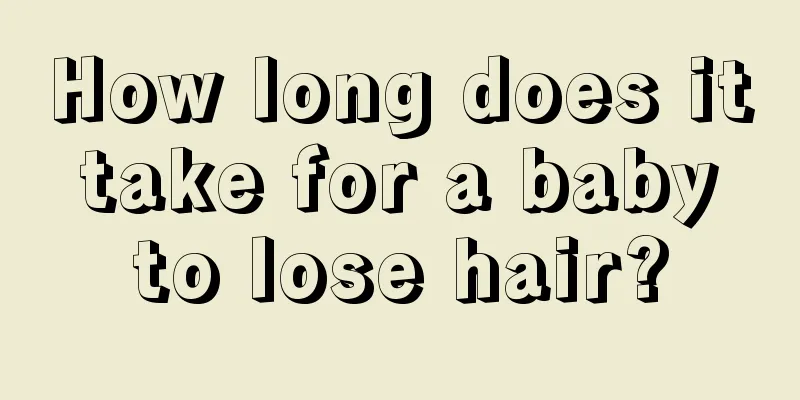Female human skeleton structure

|
The female body has 206 bones, which are connected to form the body's framework - the skeleton. It is divided into three major parts: skull, trunk bones and limb bones. Among them, there are 29 skulls, 51 trunk bones, and 126 limb bones. In fact, children's bones should be 217 to 218, and newborns have as many as 305 bones. This is because: children have 5 sacrums, which merge into one when they grow up. Children have 4 to 5 coccyx vertebrae, and one is formed when they grow up. Children have two iliums, two sciatic bones and two toe bones, which merge into two hip bones in adults. All together, children have 11 to 12 more bones than adults. Skeleton is the basis of the complexity of microbial structure, and the skeletal system is also a limiting factor in the evolution of microbial shape. Bones are hard organs that make up the endoskeleton of vertebrates. Their functions are to move, support and protect the body; produce red blood cells and white blood cells; and store minerals. Bones are made up of a variety of different shapes and have complex internal and external structures, which allow bones to remain strong while relieving weight. One of the components of bones is mineralized bone tissue, which has a hard honeycomb-shaped three-dimensional structure inside; other tissues include bone marrow, periosteum, nerves, blood vessels and cartilage. The bones of the body play the role of supporting the human body and are part of the body's endocrine system. An adult has 206 bones, which are generally connected to each other by joints and cruciate ligaments. Except for the 6 auditory ossicles which belong to the sensory organs, the bones can be divided into 23 bones of the skull, 51 bones of the trunk, and 126 bones of the limbs according to their location. Classification Tissues in bones 1. Connective tissue: bone, cartilage, fibrous connective tissue, blood vessels, blood. 2. Nervous tissue Function Applicable, maintenance, fitness, hematopoiesis (red bone marrow), storage of lipids and minerals (yellow bone marrow). type Long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones 1. Long bones - humerus, femoral head (length to width = very large) 2. Short bones - carpal bones (length to width = very small, similar to a cube) 3. Flat bones - clavicle (plate), skull, diaphragm 4. Irregular bones - spinal bones, sesamoid bones (such as patella) |
<<: Girls have pain in the lower right corner of their stomach
>>: Pain 3cm to the left of a woman's belly button
Recommend
What is the best medicine for vulvar ulcer?
The symptom of vulvar ulcer is relatively serious...
How to eat to treat high blood pressure
For more dietary recommendations, please refer to...
Is it good to drink milk during menstruation?
Milk is a very nutritious food, suitable for a wi...
Inflammation, frequent abdominal pain, ectopic pregnancy at 40 days of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the most important event in a woman&...
I am always sleepy. Am I pregnant?
Once a woman becomes pregnant, her body will send...
What are the remedies for contraceptive failure?
Nowadays, many women do not want to have more chi...
How to prevent pregnancy after giving birth?
After giving birth, women's bodies are greatl...
What to do if the hymen is broken and how to repair it
Both men and women have their own thoughts and op...
What is the disease of vulvar itching?
Women's physical health is a matter of concer...
What causes cervical erosion?
Cervical erosion is a gynecological disease that ...
Is pelvic fluid puncture painful?
Pelvic effusion is a very common disease among wo...
How to grow jasmine bought online How to grow jasmine so that it survives easily
Jasmine is a very common flower in life. Because ...
How long should I rest after a medical abortion?
After a woman becomes pregnant out of wedlock, sh...
Will my skin get worse during ovulation?
A woman's ovulation period is as regular as h...
What should I do if I just got pregnant and had a chest X-ray?
It is best not to have a chest X-ray when you are...