Anatomy of the four pairs of ligaments of the uterus

|
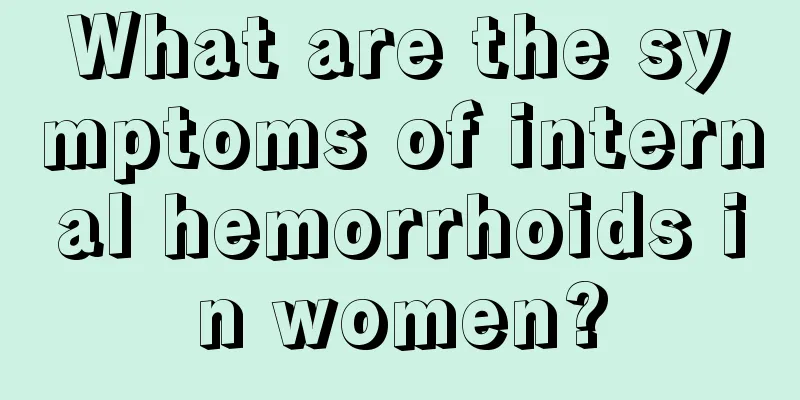
The uterine ligaments are mainly formed by the thickening of connective tissue and play a very important role in stabilizing the position of the uterine neck. There are four pairs of tendons that maintain the normal position of the uterus: round ligament, latissimus tendon, cardinal tendon and uterosacral tendon. Let's take a look at the relevant knowledge about the anatomy of the four pairs of tendons of the uterus. Anatomy of the 4 pairs of tendons in the uterus 1. Round ligament It is a perfect round strip, about 12~14cm long, composed of connective tissue and smooth muscle. It originates from the front of the uterine horns on both sides and below the proximal ends of the fallopian tubes on both sides, bends forward and downward to the pelvic walls on both sides, then passes through the groin, and ends in the middle of the upper end of the labia majora. The round ligament has the function of maintaining the anterior extension of the uterine fundus. 2. Latissimus tendon It is the wing-shaped retroperitoneal folds on both sides of the uterus, composed of the anterior, posterior, left and right lobes of the retroperitoneum and the connective tissue in between. It originates from both sides of the uterus and ends at the pelvic wall through flexion and extension. The upper edge is scattered and the lower side is connected to the retroperitoneum of the pelvic body. The broad tendon contains rich and colorful blood vessels, nerves and lymph node tissues. 3. Main tendon It is located beneath the latissimus tendon and is composed of connective tissue and a small amount of muscle tissue. It is rampant between the upper end of the cervix and the lower edge of the uterine body and the pelvic wall. There are uterine blood vessels and urethral tubes passing through later. The main tendon has the function of fixing the cervix. 4. Uterosacral tendon From the upper side behind the cervix, go around the duodenum on both sides to the muscle fascia in front of the second and third sacral vertebrae. The coupled cervix has the function of stretching backward and upward, and together with the first three pairs of tendons, it maintains the forward extension position of the uterus. These four pairs of tendons are the tendons of the uterus. Their interaction allows the uterus to maintain a normal position: when standing, the fundus of the uterus is above the bladder, the external os of the cervix is located around the level of the ischial spines, the uterine body extends forward and the cervix extends backward, and an acute angle is formed between the uterine body and the cervix. |
<<: Drinking yogurt can cure gynecological diseases
>>: Women's ovulation period picture
Recommend
Can I eat barley porridge during breastfeeding?
In order to take care of the baby in her body, br...
Brown blood on the 40th day of pregnancy_Brown blood on the 45th day of pregnancy
Pregnancy is a process that most women must go th...
Is sea buckthorn juice delicious? How to drink sea buckthorn juice
Seabuckthorn juice is a drink made with seabuckth...
Is induced abortion dangerous at eight months of pregnancy?
I believe everyone should know that induced labor...
Can I eat bitter melon while breastfeeding?
You can eat bitter melon appropriately during bre...
The difference between HPV 9-valent and 4-valent
As an effective way to prevent cervical cancer, c...
How much weight can you lose after giving birth?
We all know that after a woman becomes pregnant, ...
What could be the reason for a longer menstrual cycle and less menstrual flow?
If a woman's menstrual cycle becomes longer a...
Luo Yunbo: Near-expiry food is hotly debated, the market is hot but don’t let it go bad
Professor Luo Yunbo Honorary Vice President of Ch...
I found out I was pregnant 5 days after doing a chest X-ray
If a chest X-ray is taken, there will be radiatio...
What is the correct way to clean the vagina?
When female friends clean their vagina in life, y...
What is the health-care principle of moxibustion? What is the health-care effect of moxibustion in children?
Children's skin is very delicate, which is in...
The reason why girls have excessive oil secretion
When the weather is hot, many people's faces ...
What to do about polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a very common gyneco...
Girls acne treatment methods and care
Puberty is a process that every child goes throug...