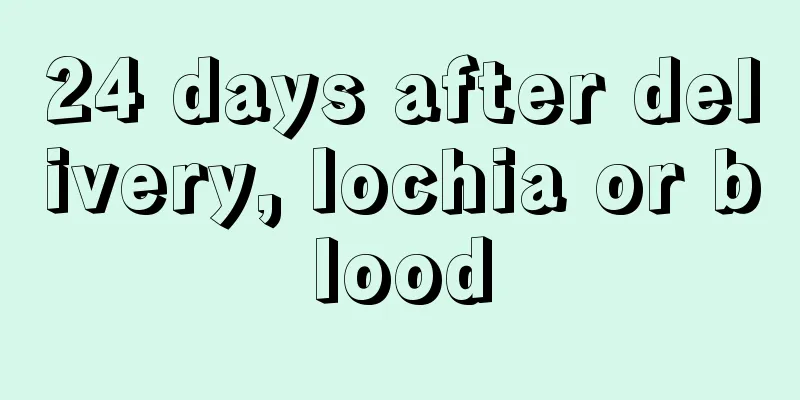Uterine size and gestational age comparison chart

|
The fetal sac chart is the initial embryonic structure, that is, the size chart of the small test tube embryo, which allows us to see whether the fetus can grow and develop normally. Pregnancy is a complicated process. After the egg is fertilized, it enters the uterine cavity, and the embryo and attachments develop rapidly to perfection. There are different changes in each week of pregnancy. 4 weeks: The fetus is only 0.2 cm. The amniotic cavity is formed just after the sperm and egg combine and the embryo implants, and its volume is not large. Ultrasound cannot clearly show signs of pregnancy. 5 weeks: The fetus grows to 0.4 cm and enters the test tube embryo stage. The amniotic cavity expands, initial cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases appear, and heart beats may be present. B-ultrasound can show a small gestational sac, which occupies less than 1/4 of the uterine cavity, or the embryonic bud and fetal heartbeat can be seen from it. 6 weeks: The baby grows to 0.85 cm, the head, brain alveoli, frontal organs, respiratory, digestive, nervous and other organs of the baby are divided, the fetal sac is clearly visible on B-ultrasound, and the fetal bud, fetal heart rate and fetal heart rate are seen. 7 weeks: The fetus grows to 1.33 cm. The test tube embryo has a human prototype. The body segments have all been divided, the limbs have separated, and the various systems are further developing. B-ultrasound clearly shows the embryo, fetal heart and fetal heart rate. The gestational sac occupies about 1/3 of the uterine cavity. 8 weeks: The fetus grows to 1.66 cm, the fetal shape is fixed, the fetal head, body and limbs can be separated, and the fetal head is larger than the body. B-ultrasound shows that the gestational sac occupies about 1/2 of the uterine cavity, the shape of the fetus and the fetal movement are clearly visible, and the yolk sac can be seen. 9 weeks: The fetus grows to 2.15 cm, the fetal head is larger than the embryo, the main manifestations of each part are clearer, the head begins to thicken, and the embryo begins to grow. B-ultrasound shows that the gestational sac almost fills the uterine cavity, the outline of the fetus is clearer, and the embryo has begun to appear. 10 weeks: The fetus grows to 2.83 cm, the fetus's internal organs have been formed, and the embryonic prototype is formed. B-ultrasound showed that the gestational sac had just begun to shrink, and a crescent-shaped embryo was visible, and the fetus was active in the amniotic fluid of the pregnant woman. 11 weeks: The fetus grows to 3.62 cm, the fetus's internal organs continue to grow and develop, and the embryo grows and develops. B-ultrasound showed that the gestational sac had completely disappeared and the embryo was clearly visible. How to read the fetal sac chart After we have confirmed the fetal sac chart, how can we accurately see the size of the gestational sac during basic prenatal examinations? The gestational sac is only seen in early pregnancy. For women with standard menstrual periods of 28 to 30 days, the gestational sac can be seen in the uterine cavity by B-ultrasound 35 days after amenorrhea. The diameter of the gestational sac is 2 cm at 6 weeks of pregnancy and about 5 cm at 10 weeks of pregnancy. The location of the gestational sac in the fundus, anterior wall, posterior wall, upper end, and middle of the uterus are all normal. It is normal for the gestational sac to be circular, oval, and clear in shape. If the gestational sac is irregular in shape, unclear, and located at the bottom, and the pregnant woman also has abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding, she may have a miscarriage. In addition, use the fetal sac to calculate (length, width and height)/3 25, mm, the result is the number of days, the fetal bud and fetal heart rate is the fetal bud and fetal heart rate length of 6.5, cm, which is the number of weeks. On the other hand, at 4 weeks, the gestational sac is not large and ultrasound cannot clearly show signs of pregnancy. At 5 weeks, a small gestational sac can be seen on B-ultrasound, which occupies less than 1/4 of the uterine cavity, or the embryonic bud and fetal heartbeat can be seen from it. At 6 weeks, the gestational sac is clearly visible on B-ultrasound, and the embryo, fetal heart rate and fetal bud are also visible. At 7 weeks, B-ultrasound clearly shows the embryo, fetal heart and fetal heart rate, and the gestational sac occupies about 1/3 of the uterine cavity. At 8 weeks, B-ultrasound showed that the gestational sac occupied about 1/2 of the uterine cavity, the shape of the fetus and the fetal movement were clearly visible, and the yolk sac could be seen. At 9 weeks, B-ultrasound showed that the gestational sac almost filled the uterine cavity, the outline of the fetus was clearer, and the embryo began to appear. At 10 weeks, B-ultrasound showed that the gestational sac had begun to disappear, and the crescent-shaped embryo was visible, and the fetus was active in the amniotic fluid of the pregnant woman. At 11 weeks, B-ultrasound showed that the gestational sac had completely disappeared and the embryo was clearly visible. |
<<: What are the symptoms of uterine bleeding?
>>: Can I have a baby if my uterus is hypoplastic?
Recommend
What are the symptoms of gynecological vulvar leukoplakia?
Gynecological diseases always trouble thousands o...
What is the normal color of female private parts?
Many women are concerned about the beauty and ski...
Can I eat hamburgers during early pregnancy?
Pregnancy is a special period. Pregnant mothers m...
What should I do if I have difficulty breathing during my seventh month of pregnancy?
When mothers become pregnant, their bodies will m...
What causes breast pain during menstruation?
Many women will experience various physical abnor...
National Eye Care Day, cartoons about myopia
In response to the requirements of the "Noti...
Average height of Chinese girls
Today is a society that blindly compares with oth...
What should I do if my skin becomes worse after abortion?
The skin is our largest organ. It not only protec...
What preparations should be made before pregnancy to give birth to a healthy baby
Pregnancy is not that easy. Now we advocate eugen...
What are the first aid measures after traumatic bleeding or fracture?
Author: Jia Dacheng, first aid expert at Beijing ...
What are the foods that are high in vitamin E? What is the function of vitamin E?
In our lives, vitamin E can not only protect our ...
What harm does abortion do to the human body?
Abortion is a surgery that women often undergo, m...
Where is the ovary located?
The uterus and ovaries are indispensable structur...
What is the reason for makeup powder floating in summer? What to do if makeup powder floats
The most annoying thing in the makeup process is ...
What to eat after morning sickness
The diet of pregnant women is related to the heal...